DBMS:
- DBMS stands for Data Base Management System. It is a group of programs that can access a collection of connected data.
- DBMS (Data Base Management System) organizes the data in the form of a table, schema, view, report, etc.
- The primary goal of a DBMS (Data Base Management System) is to provide a way to store and retrieve conveniently and efficiently.
- DBMS (Data Base Management System) is the combination of two words:
Database + Management System = DBMS
- A database is a grouping of linked data that has been saved and made accessible to numerous people for various uses.
- A database is a group of software applications that let users build and manage databases.
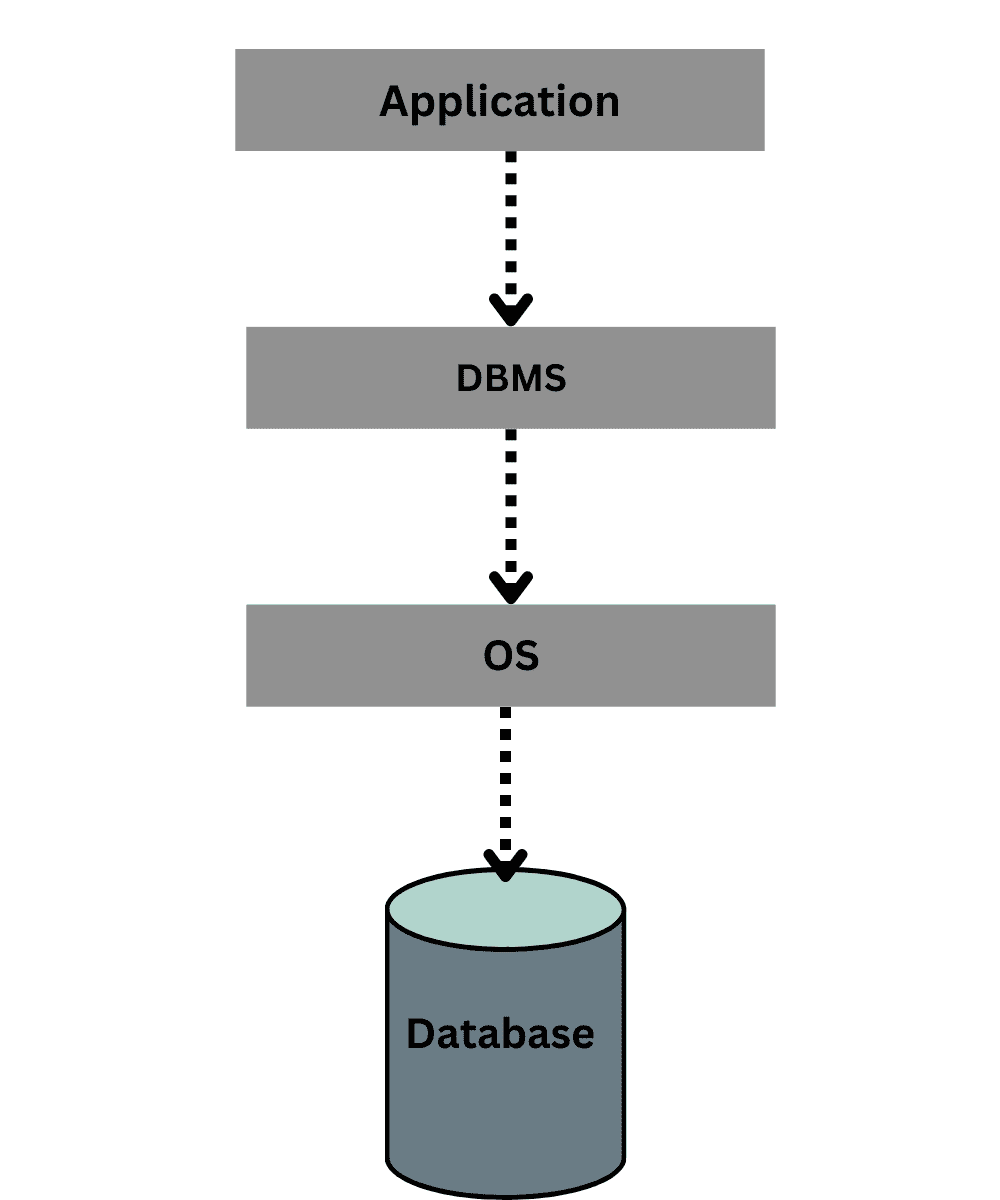
- DBMS is also an interface between the application program and the operating system to access and manipulate that database.
- DBMS (Database Management System) is software used to manage the database. For instance, prominent commercial databases like MYSQL, Oracle, etc. are used in various applications.
- Any DBMS is not the actual database. But in order to create/manage the database we need a software application that is Database Management System.
- In other words, The real database is separate from any DBMS. However, a software program known as a database management system is required in order to create and manage the database.
- DBMS (Database Management System) is a basically computer-based record system.
- A database’s goal is for its data collection to be useful for as many applications as feasible.
- Purpose of a database: The main purpose of the database is to store data and access applications. Permanent records are kept in a variety of files in a typical file processing system.
Pros:
- Reduction data redundancy
- Control data inconsistency
- Enforce standards
- Ensure data security
- Maintain integrity
- Facilitates sharing of data
Difference between the File system and DBMS
| File System | DBMS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
File System
A file is a named collection of associated data that is stored on secondary storage and includes things like:
- Magnetic Disks
- Magnetic Tapes
- Optical Disks.
A file is typically a collection of bits, bytes, lines, or records whose usage is determined by its creator and user.
File Structure
- A needed format that the operating system can understand should guide the file structure.
- Each type of file has a specific defined structure.
- Text files are collections of characters arranged in lines.
- A source file is a list of steps and operations.
- An object file is a collection of data arranged into machine-understandable blocks.
- When an operating system defines different file structures, it also contains the code to support these file structures.
- Unix and Ms-DOS support the minimum number of file structures.
Files Types
- The ability of the operating system to discriminate between different file kinds, such as text files, source files, binary files, etc., is referred to as file type.
- Numerous operating systems can handle a wide variety of files.
- The following file types are found in Ms-DOS and UNIX operating systems:
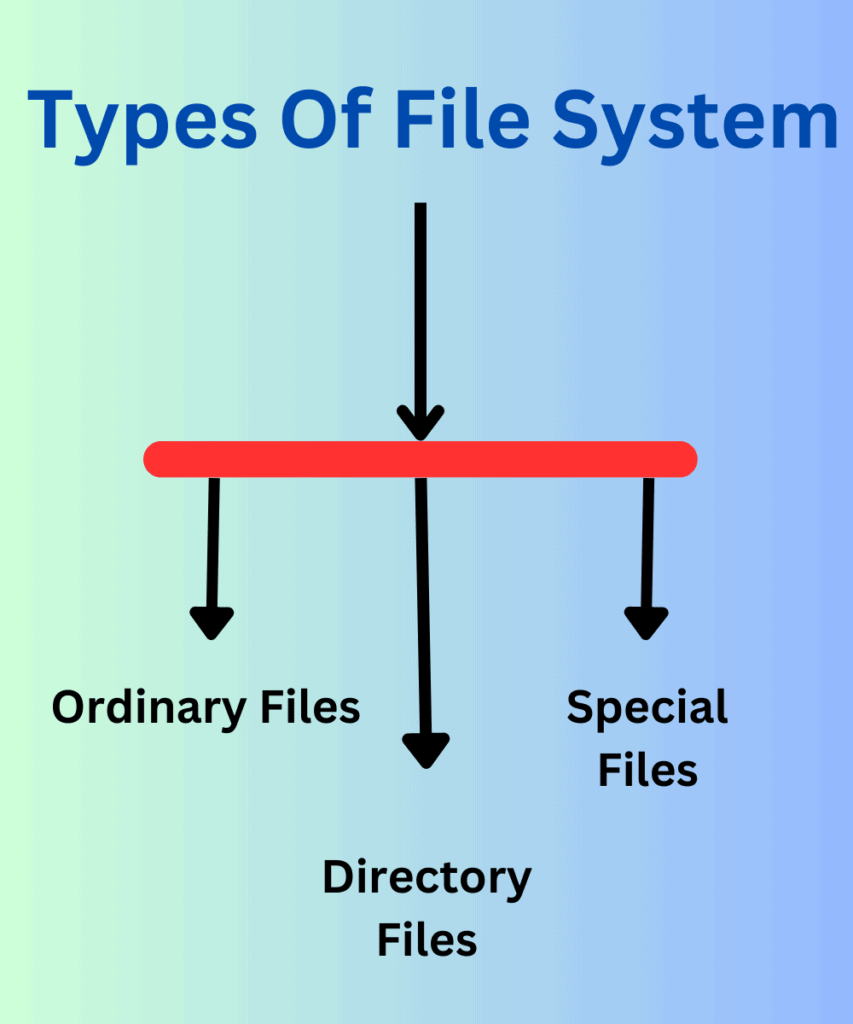
Ordinary Files:
- These files contain user information.
- These may have Text. Database or Executable program.
- The user can apply various operations on sich files like Add, Modify, Delete, or even Remove the entire file.
Directory Files:
- These files contain a list of file names and other information related to these files.
Special Files:
- These files are also known as device files.
- These files stand in for actual hardware like tape drives, terminals, printers, networks, discs, etc.
- These files are of two types:
- Character Special File: Data is handled character by character, much like it is with terminals or printers, in a character-special file.
- Block Special Files: Just like with discs and tapes, data is processed in blocks.
File Access Mechanisms
The way that a file’s records can be accessed is referred to as the file access mechanism. There are various methods for getting to files:
- Sequential Access
- Direct/Random Access
- Indexed Sequential Access
Sequential Access:
- Sequential access occurs when records are accessed one after the other, one record after another, processing the data in the file in order.
- This access strategy is the most straightforward.
- Example: This is how compilers often access files.
Direct/Random Access:
- Random access file organization provides, accessing the records directly.
- Each record has its own address on the file with the help of which it can be directly accessed for reading or writing.
- The records do not have to be in any particular order within the file or in close proximity to one another on the storage medium.
Indexed Sequential Access:
- This mechanism is built on the base of sequential access.
- Each file has an index that is constructed and contains pointers to different blocks.
- The index is searched sequentially and its pointer is used to access the file directly.
Space Allocation:
- Files are allocated disk spaces by the operating system.
- The three primary methods for allocating disc space to files are implemented by operating systems:
- Contiguous Allocation
- Linked Allocation
- Indexed Allocation
Contiguous Allocation:
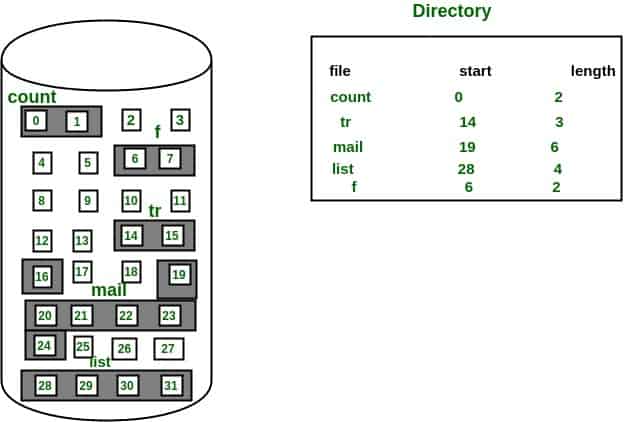
- On the disc, each file takes up a contiguous address area.
- The assigned disk address is in linear order.
- Easy to implement.
- The main problem with this kind of allocation mechanism is external fragmentation.
Linked Allocation:
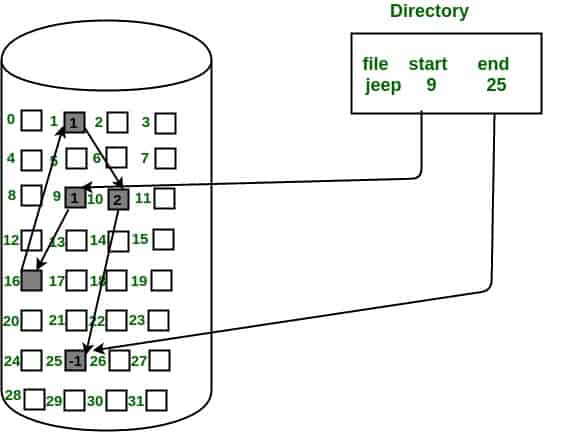
- Each file carries a list of links to disk blocks.
- The directory contains a link/ pointer to the first of a file.
- No external fragmentation
- Effectively used in sequential access files.
- Inefficient in case of direct access file.
Indexed Allocation:
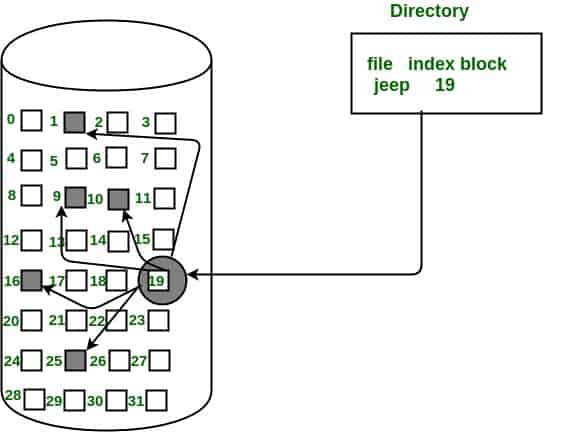
- Provides solutions to problems of contiguous and linked allocation.
- All file pointers are compiled into an index block.
- Each file has a unique index block that contains the addresses of the disc space the file has taken up.
- The directory contains the address of index blocks of files.
Characteristics of a file system
- The following are significant components of the file system:
- You can save data in a collection of files to make life easier.
- Data files are interdependent.
- The files were created using COBOL and C/C++ languages.
- Support For Shared File Systems
- Quick File System Recovery.